Search engine optimization has different perspectives. One important factor in optimizing a website is to regularly clean up the content to keep it up to date. You can compare the contents of the website with the food we will be consuming. When it is fresh, it is very attractive, which attracts many visitors. However, when it becomes obsolete, it becomes unwanted and undesirable, causing ratings to drop.
SEO Offer: Optimize your website with a special 14-day free trial of SEMrush Pro.
Why clean up old content?
Nowadays, the importance of content has become more apparent, as has finding the right keyword to use. However, in order for a website to maintain consistent rankings, it is important to clean up old content on a regular basis. But how does it help SEO in terms of conversions, backlinks, rankings, clicks, impressions, and traffic?
Before you start cleaning up your content, you should know why you are doing it in the first place.
- Make the best use of Googlebot to crawl your site.
- Eliminate the issue of having two content on the same topic that could cause Google to rank the page you don’t want instead of the one you want.
- Reduce index bloat due to too many thin pages in Google search.
- Users are taken to subtle or less useful pages.
- Your backlinks are affected as thin pages affect the visibility of pages with long content.
Index Inflating Example
Index bloat is an SEO term used to refer to the availability of too many pages indexed by Google while there are fewer pages on the site. This can happen due to the use of taxonomies such as categories, tags, and archives. While archive pages on your site, such as a blog feed, help offer a feed to readers, they create too many pages on your site. Let’s look at an example of using the WordPress content management system:
- Page > page1
- Page 1 Category > Category 1 and Category 2
- Page1 Tags > tag1, tag2, tag3 and tag4
- Author> author archive
- date > date archive
- Blog > blog archive
- RSS > blog feed, category feed and 4 tag feed
As you can see, you can create entries in 16 different places on one page. The problem occurs when you use category tags or channels incorrectly. You need to group similar content so that users can easily read based on their interests. However, using too many tags will result in a separate tag page with one or two pages listed. When these taxonomy pages are static, Google will start showing up in search results instead of your original page.
This is an unintended example due to misuse of taxonomies and archives. However, there are times when thin content is created specifically to increase the number of pages on a site. These thin content pages will rank lower by overtaking your valuable content.
How to find low value content?
This depends on the size of your website and a detailed analysis of your content is needed to determine what content to opt out of. The focus is on content that is detrimental or does not affect SEO. As a general rule, your content should contain valuable, credible, and useful information that can help search engines interpret your content as quality content.
However, finding low-value content on your site is not an easy task. You can use the following tools in combination to rate pages on your site:
- Use data from Google Analytics to find pages with low traffic. However, you won’t be able to find pages that don’t have any visitors at all.
- When you are using WordPress or other content management systems, look for plugins to help you display pageviews for each page/post. For example, the popular newspaper WordPress theme records page views and is displayed in the WordPress admin panel for each post. You can filter pages with 0 and low views.
- Find the number of words on each page to filter out thin content with less than 300 words.
- Analyze taxonomy and archive pages to find duplicate pages.
When you find low value content, check the relevant keywords on Google to validate the search results. If you see search results showing low-value content instead of the intended pages, then you can assume that this has begun to affect your site’s ranking.
Planning for content removal
After evaluating the content, below are some of the actions you can take.
1. Do nothing
As mentioned, finding the value of a page is not an easy task if you have less traffic and there is relevant content on the page. There are many blogs available on the Internet, so don’t expect every page on your site to rank at the top of Google searches. If you’re not sure if a page is outdated, thin, or duplicated, you don’t need to take any action if your old content is of little value but does no harm.
2. Update old content
Not all old pages deserve deletion, there is old content that just needs to be updated. These content types should contain relevant information and value. It can have backlinks from authoritative sites and still provide good stats.
For example, if your blog has an article about ” updating the google algorithm “, then you should be aware that such articles will be updated frequently as they become outdated over time. As a result, it will remain relevant to the reading audience.
Converting old articles to a new publication isn’t easy because it takes a lot of work, but it’s useful because it makes them more valuable and relevant. However, be sure to use a 301 redirect on the old URLs to direct traffic to the newly updated post.
3. Remove low value content.
Another option that you can use when cleaning up old content is a complete deletion. This is to be done when the article ceases to have value or, even worse, damages your site’s SEO. For example, if you wrote an article before the Google Panda update where keyword stuffing was the top SEO strategy regardless of the quality of the content. You may want to delete it to avoid the Panda update effect, as the article could lose its value, especially if it was of poor quality or thin.
4. Combine pages
- Combine similar content on the same topic into one new content page.
- Delete or merge taxonomy and archive pages. For example, a single-author site should not have a separate author archive or date archive, as it would be the same as a blog index page.
Informing the search engine about your actions
Removing content by itself will not shrink it; you also have to make sure that search engines like Google also know that those pages no longer exist by instructing the search bot to read. This will prevent further indexing of deleted pages. How do you do it?
redirect
After updating old content or merging old small posts into new content, you need to tell search engines that the URL has changed. A 301 redirect directs search engines to new content from older posts. This is important so that you don’t lose the page rank and backlink value of the deleted pages.
Showing 404 or 410
Old, non-consequential content that has been removed should be accompanied by a 404 Not Found code, which will tell search engines that the content is no longer available and was intentionally removed. After this code is pasted, the page will return a 404 Not Found message to search engines.
Initially, the page may still show up on search pages, but it will eventually disappear and stop showing up. Another code you can use is 410 to tell search engines that the content is gone for good.
3. No index meta tag
Another way to keep your old content from search engines is to add a no-index tag, which tells search engines to ignore the page. You can add the robot HTML meta tag to the title section of the page with the noindex parameter to tell Google not to index in search results.
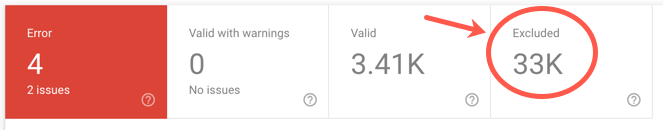
You can view all non-indexed pages on your site in the Coverage section of Google Search Console and analyze which pages are getting traffic. This will help you, if necessary, take the necessary actions to return these pages to the search results.
4. Use the canonical URL
Another option is to set up a canonical URL if you really want to keep two pages with the same content on your site. While you can have two pages with two different URLs, you can tell search engines that both pages come from the same source. You can do this by adding a canonical meta tag to duplicate pages.
Conclusion
Regular maintenance of your site should include cleaning your site of old content. Not periodically checking your archive for old content can create unnecessary problems for you. This outdated content may contain inappropriate or misleading information for your audience. This can eventually affect your page ranking due to content that search engines deem not valuable or useful. This is bad for your site’s SEO, so you need to access and evaluate your old content and determine what you need to do with it. The result of your evaluation will influence your decision to remove or update your content.